Lesson 03 - Practice Problems (KEY)#
For the circuit at the bottom of page 2, solve the table for the empty cells.
Variable |
Circuit #1 |
Circuit #2 |
Circuit #3 |
Circuit #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
R1 |
500Ω |
13.3Ω |
2KΩ |
100Ω |
I1 |
40mA |
600mA |
6mA |
200mA |
V1 |
20V |
8V |
12V |
20V |
P1 |
800mW |
4.8W |
72mW |
4W |
For the circuit below, solve the table for the empty cells.
Variable |
Circuit #1 |
Circuit #2 |
Circuit #3 |
Circuit #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
R1 |
50 kΩ |
53.3MΩ |
2MΩ |
400Ω |
I1 |
100µA |
15nA |
500µA |
150mA |
V1 |
5V |
800mV |
1kV |
60V |
P1 |
500µW |
12nW |
500mW |
9W |
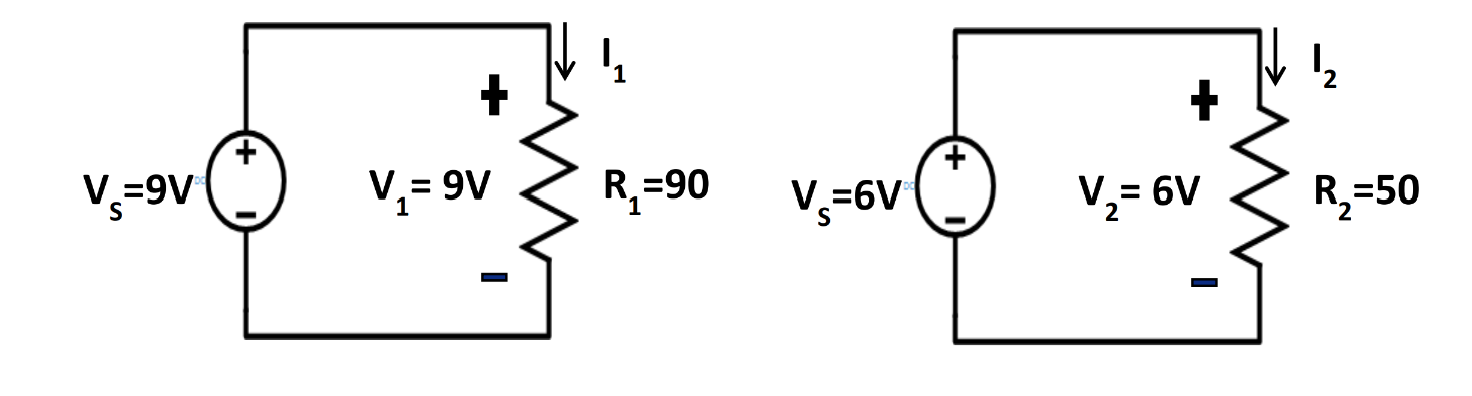
Which flashlight design is better if your main concern is power consumption?
Option 1 |
Option 2 |
|---|---|
R1 = 90 Ω |
R1 = 50 Ω |
V1 = 9V |
V1 = 6V |
P1 = 900mW |
P2 = 720mW |
Design 2 is better because 720mW<900mW
Two light bulbs, one rated at 50 W and the other rated at 100 W bulb are each connected to a 110 V source. Which bulb draws more current?
\(P_{1}\ = \ 50\ W\ = V_{1}*I_{1} \rightarrow I_{1} = \frac{50\ W}{110\ V} = 455\ mA\)
\[P_{2}\ = \ 100W\ = \ V_{2}*I_{2} \rightarrow \ I_{2} = \frac{100\ W}{110\ V} = 909\ mA\]Bulb 2 draws more current because 909 mA is greater than 455 mA
The lighting for a new UAS control console is modeled as a voltage source and a resistor, as shown below. For each of the following proposed options, find the unknown value. If the sole measure of merit is to minimize current, which of the six options is best?
Variable |
Circuit #1 |
Circuit #2 |
Circuit #3 |
Circuit #4 |
Circuit #5 |
Circuit #6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
R1 |
5.4 kΩ |
4.8 kΩ |
7.4 KΩ |
100 Ω |
667Ω |
1.125kΩ |
I1 |
2 mA |
5 mA |
1.08mA |
15mA |
8mA |
|
V1 |
10.8V |
24V |
8V |
Circuit #4 is best because 1.04 mA is the smallest current
The GPS receiver for an experimental cruise missile can be modeled as a single resistor connected to a voltage source. Given the six designs below, if the sole measure of merit is to minimize power consumption, which of the designs is best?
Variable |
Circuit #1 |
Circuit #2 |
Circuit #3 |
Circuit #4 |
Circuit #5 |
Circuit #6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
R1 |
100Ω |
300Ω |
8.2 KΩ |
4.8 kΩ |
1.5 kΩ |
1.2 kΩ |
I1 |
15 mA |
8 mA |
5 mA |
12 mA |
6mA |
|
V1 |
1.5 V |
2.4 V |
41V |
57.6V |
9V |
12V |
P1 |
22.5mW |
19.2mW |
205mW |
691.2mW |
54mW |
120mW |
Circuit #2 is best because its power consumption of 19.2mW is the smallest
Given the following model of the cooling system of a laptop computer, clearly articulate how the current in the circuit would change if the resistance of the fan doubled from 1.5 kΩ to 3.0 kΩ .
Resistance and current are indirectly proportional, as can be seen in Ohm’s Law \(\left( I = \frac{V}{R} \right)\). Since voltage is remaining constant, and resistance is going up, current must go down.
Performing the calculations, we get:
Given the following model of an electric clock, clearly articulate how the power consumed by the clock would change if the voltage source decreased from 9.0 V to 4.5 V.
Power is proportional to the square of voltage, as can be seen by the equation combining Ohm’s Law and the Power Equation \(\left( P = \frac{V^{2}}{R} \right)\). If voltage goes down, then the power consumed will also go down. More specifically, if the voltage is halved (like in our example above), the power will be reduced by the square of that, meaning it will be reduced by a factor of 4.
Performing the calculations, we get:
To be effective as an illumination source, the thunderstorm lighting of an aircraft modeled as a single 10 Ω resistor connected to a voltage source must consume a minimum of 250 W.
(a) Would a 28-Volt battery be an acceptable voltage source?
\[P = \ \frac{V^{2}}{R} = \frac{{(28\ V)}^{2}}{10\ \Omega} = 78.4W < 250W - no,\ not\ acceptable!\]Other method: \(V = \sqrt{P*R} = \sqrt{250W*10\Omega} = 50\ V > 28\ V - no,\ not\ acceptable!\)
Since the power consumed by the lighting system is less than the minimum requirement of 250 W when using a 28-V battery, the 28-V battery is not an acceptable voltage source.
(b) What is the minimum allowable voltage for the voltage source?
A background light for a home stereo system is limited to 1 W to prevent damage to the stereo housing. The light is modeled as a single 100 Ω resistor.
(a) Is a current of 9.2 mA acceptable?
\(P\ = \ I^{2}R\ = (9.2\ mA)^{2}*100\ \Omega = (0.0092\ A)^{2}*100\ \Omega\ = \ 8.464mW\) – yes, this is acceptable.
Other method: \(I = \ \sqrt{\frac{P}{R}} = \sqrt{\frac{1W}{100\Omega}} = 100mA > 9.2\ mA\) – yes this is acceptable
When using a current of 9.2 mA, the power consumed by the background light is 8.464 mW. Since this power consumed is less than the maximum limit of 1 W, the current is acceptable.
(b) What is the maximum allowable current in the circuit?




