Xilinx Vivado#
Create a new Vivado Project#
In “Quick Start” click Create Project >
In wizard, click Next
Name your project and pick a location.
If you cloned a repository first, pick that folder!
Uncheck “Create Project subdirectory” if you already selected a folder
RTL Project, do not check either box
Add Sources, click Add Files and pick your source VHDL files.
Uncheck Copy sources into project, then click Next.
Add Constraints, Add Files, select your
.xdcfile, then Next.Default Part, click Boards tab at the top
Search for Basys3 (or whatever board you are using) and select it (will highlight blue). If the Basys3 board does not show up, click the Refresh button in the bottom left corner.
Next and Finish.
If needed, add simulation files using steps in Manually add files to Vivado Project
Manually add files to Vivado Project#
By convention (and for working nicely with git) we add
source files to src/ and if it is a hardware description file then to src/hdl/
(there are other source files in advnaced projects that are not HDL).
Once a file is in that location, add it to a Vivado Project by:
On the leftmost pane (Flow Navigator) of Vivado, under PROJECT MANAGER, click on Add Sources
Select the appropriate radio button.
“Add or create constraints” for an
.xdcfile“Add or create design sources” for source file
“Add or create simulation sources” for a
_tb.vhdfile
Click on Add Files
Select your file
Make sure to UNCHECK “Copy sources into project”
Click Finish
You should now see the file in the Sources tab.
The VHDL module should now be listed in your Sources sub-window. The bolded name is based on the entity name.
This will also make a change in your .xpr file that you will need to commit as well.
Board files#
If you have not already installed the board files (should have been done as part of Lab0), do this. It assumes Vivado is installed at the default location.
Close all Vivado windows
Navigate to
C:\Xilinx\Vivado\2018.2\data\boards\board_files\Create a directory named
basys3\C.0\Go to XilinxBoardStore. Note the tag 2018.2 should match your Vivado version.
Copy all four of those files (3 .xml and 1 .json) to
C:\Xilinx\Vivado\2018.2\data\boards\board_files\basys3\C.0\Repeat for any other boards you plan to use
Restart your computer, just to make sure
Vivado should now be able to see the board and present it as an option if you create a new project or modify project settings.
Below this is for advanced usage only
Write a TCL file for use with Git#
In order to work more seamlessly with Git, we place all of our .vhd and constraint files
in src/hdl/. Otherwise, Vivado will place them in unexpected nested directories.
Unfortunately, when we do this, Vivado will not know where to find our files unless we tell Vivado where they are either manually or with a TCL file using TCL Batch Mode.
To write a TCL file#
Vivado will write the file for you but you need to make a few changes.
In Vivado **File –> Project –> Write Tcl
Select an output file, such as
build.tclin the root directory of your projectUncheck “Copy sources to new project”. You can optionally check “Write all properties”
If the file already exists it is ok to overwrite.
No need to open the file.
Edit TCL file to work with Git#
This example assumes you named your file build.tcl.
How to use git diff#
If you are working from an existing tcl file, it is easiest to work with git diff
to see what changed. Both options below show additions in green and deletions in red.
Either open the build.tcl file in VS Code and use the Source Control Changes option to view, as shown in Fig. 43.
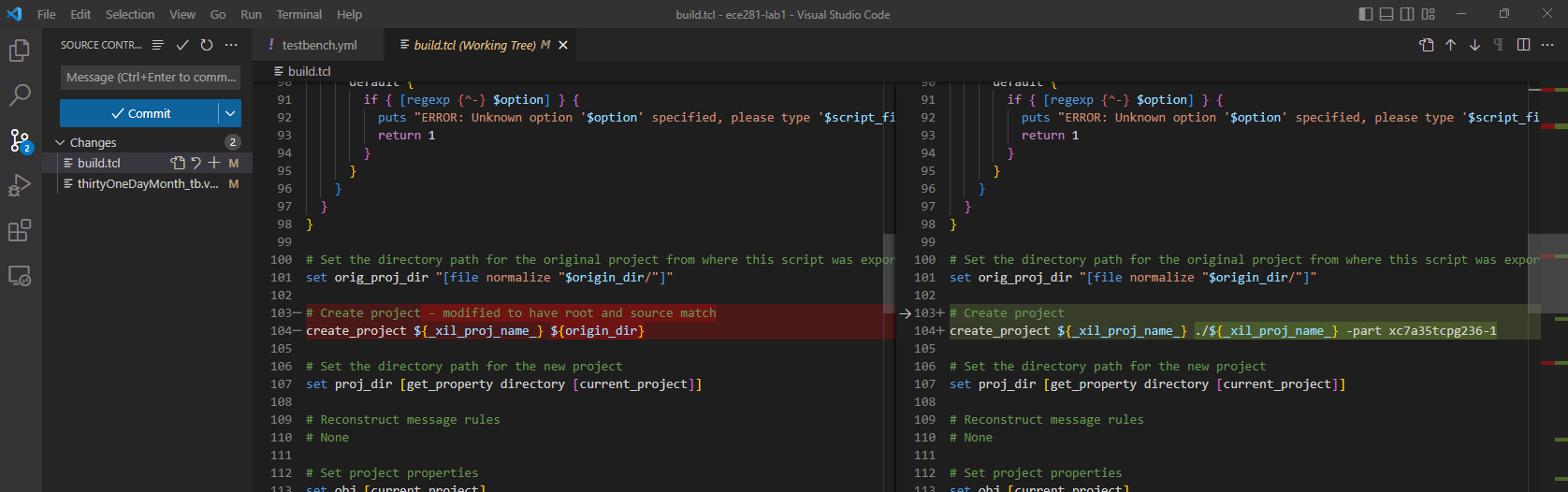
Fig. 43 Using VS Code to view TCL diffs#
Or from Git Bash use the command below to produce output similar to Fig. 44
git diff build.tcl
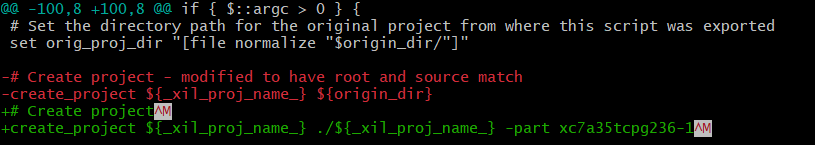
Fig. 44 Using Git Bash to view the TCL diffs#
What to actually change#
In the comments, change the absolute path to a relative path.
# CHANGE
# "C:/Users/User.Name/vivado/bcy/ece281-lab1/src/hdl/thirtyOneDayMonth.vhd"
# TO
# "/src/hdl/thirtyOneDayMonth.vhd"
Update the relative path to project files.
The -part xc7a35tcpg236-1 refers to the Basys3 board.
## CHANGE
# Create project
create_project ${_xil_proj_name_} ./${_xil_proj_name_} -part xc7a35tcpg236-1
## TO
# Create project - modified to have root and source match
create_project ${_xil_proj_name_} ${origin_dir} -part xc7a35tcpg236-1
It is worth doing a sanity check on any other git diffs, but the rest of the file is probably ok as is.
To use a TCL file#
Clone the repo
Open Vivado 2018.2 (but not the project)
From the Vivado welcome screen, select Window –> Tcl Console
In the tcl console at the bottom of the screen
cdto your project directoryIn the console enter
source <yourproject.tcl>The project should build and you should see entities populated in the Sources window
Alternatively, use a bat file such as below:
@echo off
echo Building Vivado projeect from TCL file
echo ----------------------------------------
set VivadoPath="C:\Xilinx\Vivado\2018.2\bin\vivado.bat"
:: chcek if vivado path is valid
if not exist %VivadoPath% (
echo Vivado path is not valid
exit /b 1
)
set TCL="build.tcl"
:: check if TCL file is valid
if not exist %TCL% (
echo TCL file is not valid
exit /b 1
)
:: run vivado in batch mode to build project
call %VivadoPath% -mode batch -source %TCL%
echo ----------------------------------------
:: wait for a keypress
PAUSE
Inspiration taken from this fpgadeveloper post
