a. Find \(I_{S}\)
We reduce the circuit step by step by identifying series and parallel combinations.
First, combine the resistors that are in series:
\[
R_{\text{eq},1} = R_3 + R_4 + R_5
\]
Next, combine this equivalent resistance in parallel with \(R_2\):
\[
R_{\text{eq},2}
= \left( \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_{\text{eq},1}} \right)^{-1}
\]
Substituting for \(R_{\text{eq},1}\) gives
\[
R_{\text{eq},2}
= \left( \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3 + R_4 + R_5} \right)^{-1}
\]
Finally, add the remaining series resistors to obtain the total equivalent resistance:
\[
R_{\text{eq}}
= R_1 + R_{\text{eq},2} + R_6
\]
or, written in a single expression,
\[
R_{\text{eq}}
= R_1
+ \left( \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3 + R_4 + R_5} \right)^{-1}
+ R_6
\]
\[
= 8.71\,\Omega
\]
\[
I_{S}
= \frac{V_{S}}{R_{eq}}
= \frac{5\,\mathrm{V}}{8.71\,\Omega}
= 574\,\mathrm{mA}
\]
b. Find the power consumed by \(R_{2}\)
Current divider, where \(R_{2,3,4,5}\) is the equivalent resistance of the parallel portion:
\[
I_{2}
= I_{S}\frac{R_{2,3,4,5}}{R_{2}}
= (574\,\mathrm{mA})\frac{1.71\,\Omega}{2\,\Omega}
= 491\,\mathrm{mA}
\]
\[
P_{2}
= I_{2}^{2}R_{2}
= (0.491\,\mathrm{A})^{2}(2\,\Omega)
= 482\,\mathrm{mW}
\]
Using a voltage divider:
\[
V_{2}
= V_{S}\frac{R_{2,3,4,5}}{R_{eq}}
= (5\,\mathrm{V})\frac{1.71\,\Omega}{8.71\,\Omega}
= 982\,\mathrm{mV}
\]
\[
P_{2}
= \frac{V_{2}^{2}}{R_{2}}
= \frac{(0.982\,\mathrm{V})^{2}}{2\,\Omega}
= 482\,\mathrm{mW}
\]
Find \(R_{eq}\), \(I_{S}\), \(P_{2}\), and \(P_{Total}\).
\[
R_{eq}
= R_{1} + R_{2,3}
= 50\,\Omega + \left(\frac{1}{500\,\Omega} + \frac{1}{500\,\Omega}\right)^{-1}
= 300\,\Omega
\]
\[
I_{S}
= \frac{V_{S}}{R_{eq}}
= \frac{1.5\,\mathrm{V}}{300\,\Omega}
= 5\,\mathrm{mA}
\]
\[
P_{Total}
= I_{S}V_{S}
= (5\,\mathrm{mA})(1.5\,\mathrm{V})
= 7.5\,\mathrm{mW}
\]
\[
I_{2}
= \frac{R_{2,3}}{R_{2}}I_{S}
= \frac{250\,\Omega}{500\,\Omega}(5\,\mathrm{mA})
= 2.5\,\mathrm{mA}
\]
\[
P_{2}
= I_{2}^{2}R_{2}
= (2.5\,\mathrm{mA})^{2}(500\,\Omega)
= 3.125\,\mathrm{mW}
\]
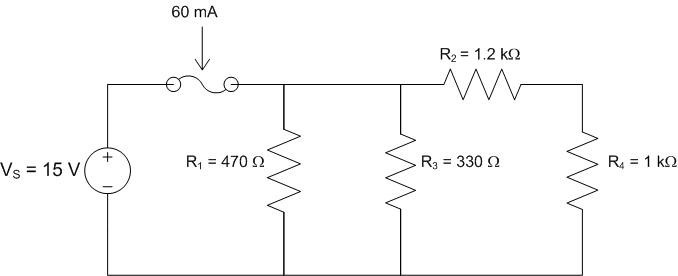
Find the equivalent resistance and determine if the fuse rating is high enough.
\[
R_{\text{EQ}}
= \left(
\frac{1}{\dfrac{1}{R_1} + \dfrac{1}{R_3} + \dfrac{1}{R_2 + R_4}}
\right)
\]
\[
R_{\text{EQ}}
= \left(
\frac{1}{\dfrac{1}{470\,\Omega}
+ \dfrac{1}{330\,\Omega}
+ \dfrac{1}{1.2\,\text{k}\Omega + 1\,\text{k}\Omega}}
\right)
= 182.78\,\Omega
\]
\[
V_S = I_S R_{\text{EQ}}
\]
\[
I_S
= \frac{V_S}{R_{\text{EQ}}}
= \frac{15\,\text{V}}{182.78\,\Omega}
= 82.10\,\text{mA}
\]
No, the fuse rating is not high enough.
\[
82.1\,\text{mA} > 60\,\text{mA}
\quad \Rightarrow \quad \text{the fuse will pop}
\]
The fuse should be designed between
\[
I_{\text{fuse,min}} = 1.1 \times 82.1\,\text{mA} = 91\,\text{mA}
\]
and
\[
I_{\text{fuse,max}} = 1.5 \times 82.1\,\text{mA} = 123\,\text{mA}.
\]
Choose a 100mA circuit breaker from the parts bin.
Determine the appropriate resistor so the voltage across the load is 45 V.
\[
V_{Adapter}
= V_{S} - V_{Lamp}
= 115\,\mathrm{V} - 45\,\mathrm{V}
= 70\,\mathrm{V}
\]
\[
R_{Adapter}
= \frac{V_{Adapter}}{I_{S}}
= \frac{70\,\mathrm{V}}{2\,\mathrm{A}}
= 35\,\Omega
\]