Practice Problems (KEY)#
Plot the following equations:
a)
\(v(t) = -2 + 2\cos(360^\circ \cdot 100\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\)
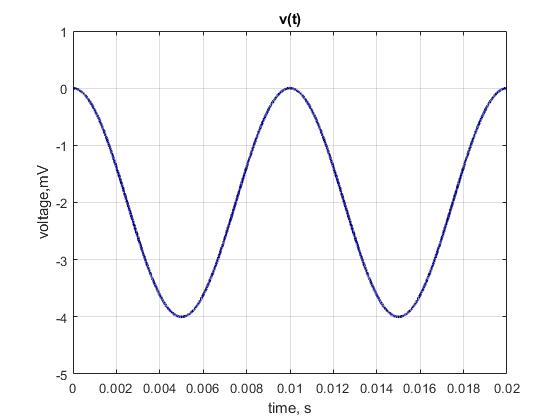
b)
\(v(t) = 2\cos(360^\circ \cdot 10\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\)
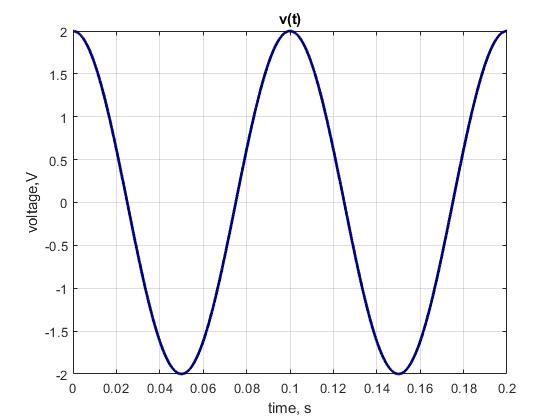
c)
\(v(t) = 4\cos(360^\circ \cdot 1\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\)
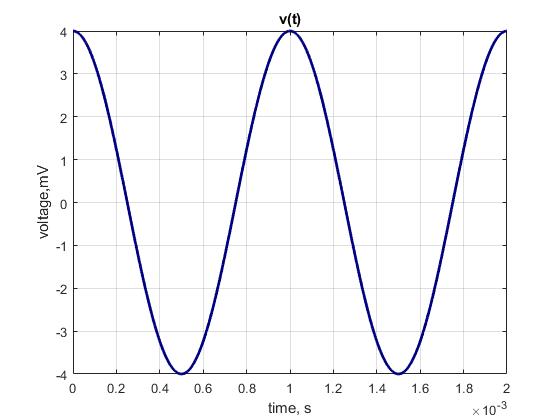
d)
What equation is associated with the graph?
e)
What equation is associated with the graph?
If
\(v_{S}(t) = 4 + 8\cos(360^\circ \cdot 10\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\),
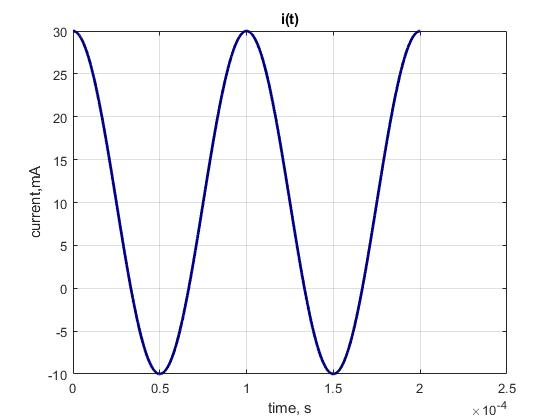
graph \(i_{X}(t)\) for the signal below.
The current is given by Ohm’s Law:
Substitute the source voltage and equivalent resistance:
Simplifying,
or, expressed in milliamps,
Find the power consumed by the circuit below given \(V_{S} = 1.5\ \mathrm{V}\).
The equivalent resistance is
The source current is
The total power supplied is
Find the average power consumed by the circuit below given:
The source voltage is given by
The source current is
The RMS current is
The RMS voltage is
The average power consumed is
Compare the power consumed by the two circuits above.
The power consumed is the same.
What is \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{Hz}}\) equivalent to?
a. s - Correct Answer
b. 1/s
c. f
d. None of the above
A 9 V battery is connected to a resistor that consumes 7.22 mW of power. Which AC source would cause the same resistor to consume 7.22 mW of average power?
a. \(7.22\cos\!\left(360^\circ \cdot 2\,\text{kHz} \cdot t\right)\,\text{mV}\)
b. \(9\cos\!\left(360^\circ \cdot 2\,\text{kHz} \cdot t\right)\,\text{V}\)
c. \(7.22\,\text{mV}_{\text{RMS}}\)
d. \(9\,\text{V}_{\text{RMS}}\) - Correct Answer
A B-52 generator produces the signal
\(v(t) = 290\cos(360^\circ \cdot 400\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\).
a) Graph the signal as a function of time.
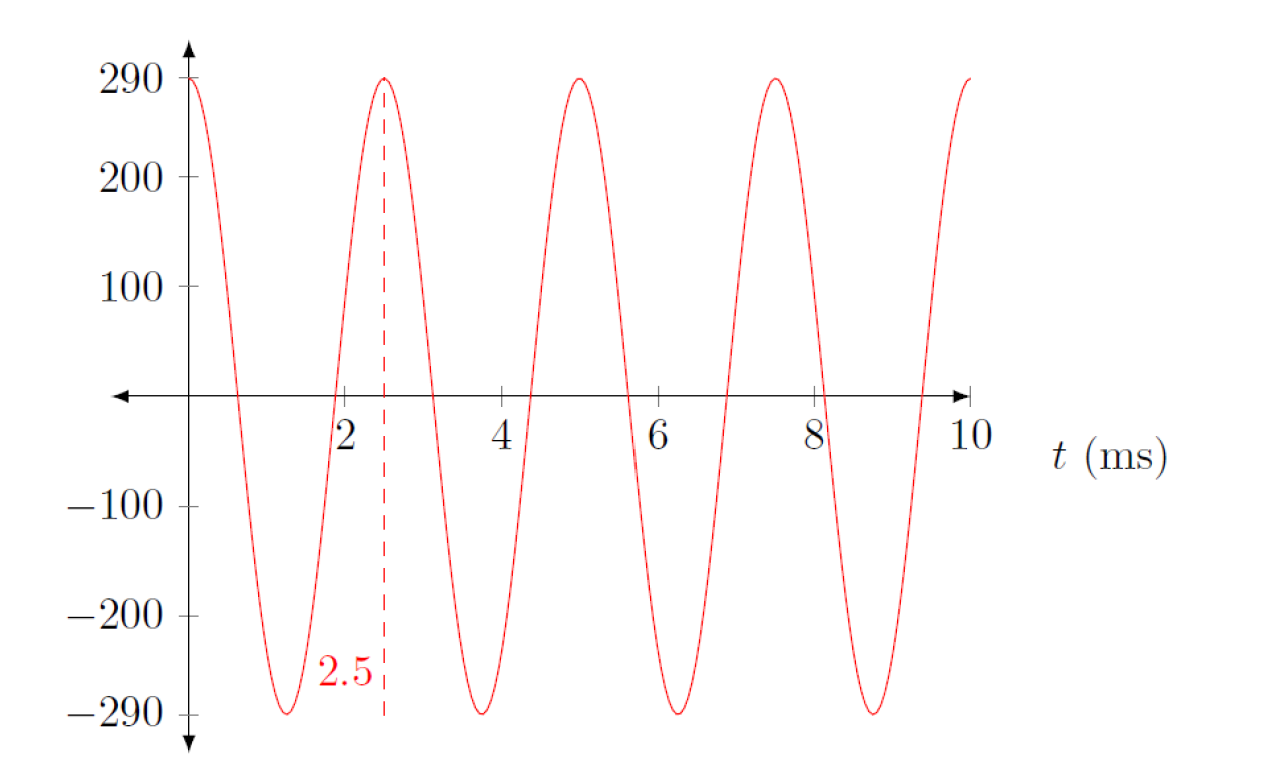
b) What is the RMS voltage for the generator?
Solution:
The amplitude of the signal is \(A = 290\,\text{V}\). Recall the RMS formula for a sinusoidal signal with a possible DC bias:
In this case, \(V_{\text{bias}} = 0\), so the expression simplifies to:
Substituting the given amplitude:
The fuse for a 2000-lb general-purpose bomb includes a spinner producing
\(v(t) = 15\cos(360^\circ \cdot 2\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\).
The arming circuit is modeled as three resistors. Graph the current signal \(I_{S}(t)\).
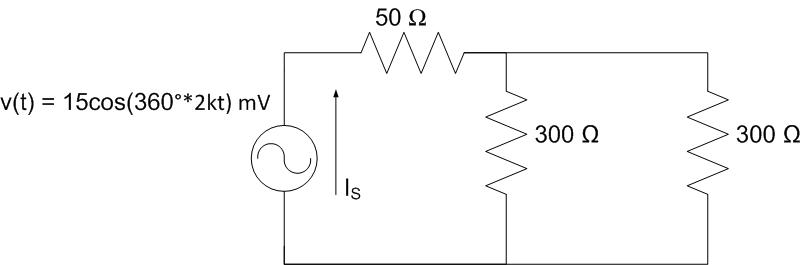
Solution:
To determine the current out of the spinner, we must first find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. The equivalent resistance is:
Therefore, the equivalent circuit is a single resistor of \(200\,\Omega\) driven by the source
Now, we find the source current \(I_S(t)\) using Ohm’s Law:
Using this result, we can easily graph the current signal. Since there is no phase shift (i.e., \(\phi = 0\)), the period of the signal is
The resulting waveform for \(I_S(t)\) is a cosine signal with a peak amplitude of \(75\,\mu\text{A}\) and a period of \(500\,\mu\text{s}\).

Which of the two sources below produces more average power?
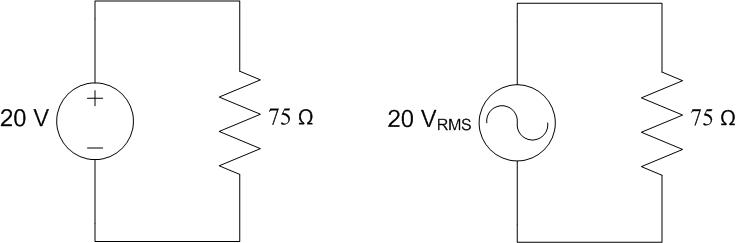
Solution:
In the circuits above, we have a DC source and an AC source. The DC source is \(20\,\text{V}\), and the AC source is \(20\,\text{V}_{\text{RMS}}\). Both sources are connected in parallel with a \(75\,\Omega\) resistor.
We know that the power supplied equals the power consumed.
For a DC source, the power delivered to a resistive load is given by:
For an AC source, the average power delivered to a resistive load is given by the same expressions, except that RMS values are used instead of peak values:
Since the RMS value of an AC source is the DC-equivalent value in terms of power delivery, a \(20\,\text{V}\) DC source and a \(20\,\text{V}_{\text{RMS}}\) AC source deliver the same average power to the same resistive load.
Therefore, the two sources supply identical average power to the \(75\,\Omega\) resistor.
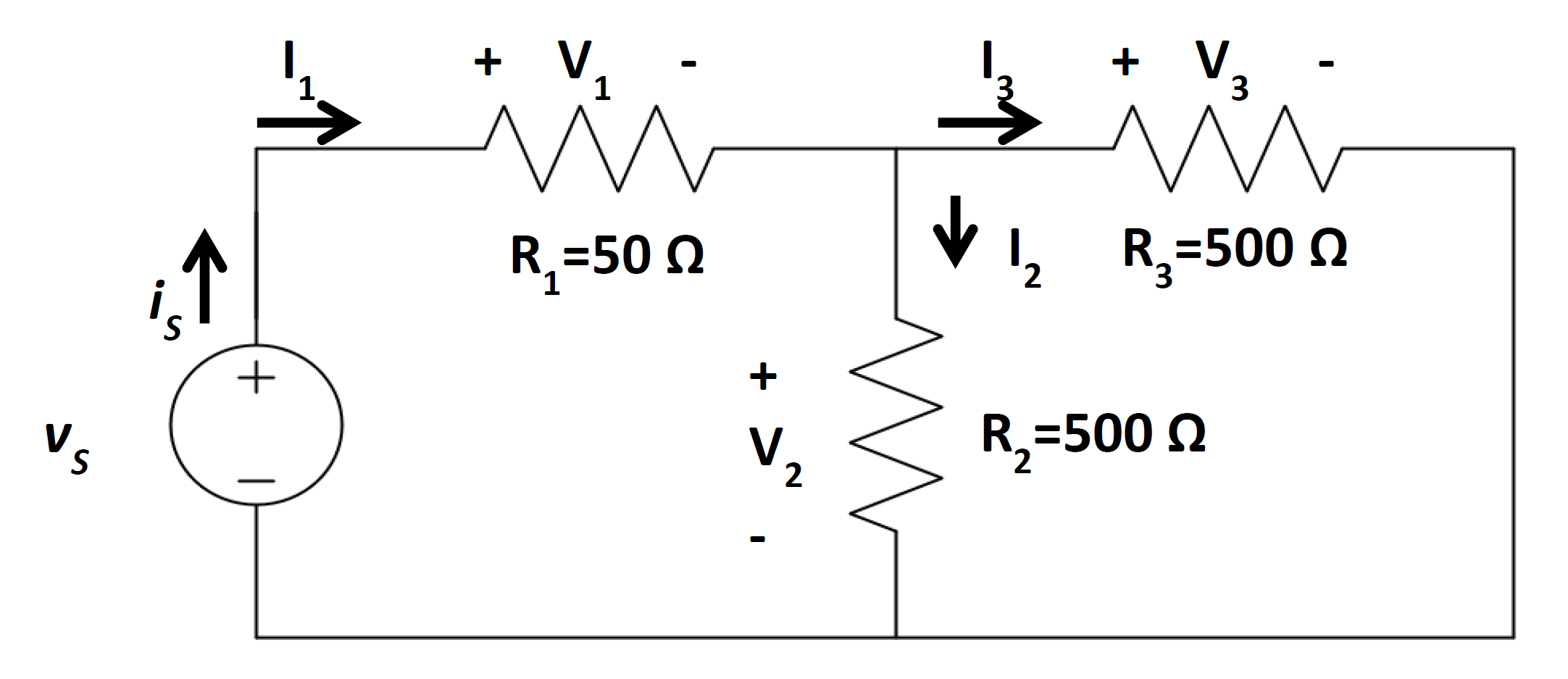
The circuit below has a current source providing
\(i(t) = 11.75\cos(360^\circ \cdot 50\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{A}\).
Find \(v_{1}(t)\).
Solution:
If we can find the current through the \(6\,\Omega\) resistor, we can also find the voltage drop across it. In this circuit, all resistors are in parallel, so we can use a current divider to find the current through the \(6\,\Omega\) resistor.
Recall the current divider equation:
Here:
\(I_x\) is the current through the \(6\,\Omega\) resistor (denoted \(I_1\)),
\(R_x = 6\,\Omega\),
\(I_{\text{Total}} = i(t)\), the current provided by the source.
First, find the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors:
Now substitute into the current divider equation:
Finally, use Ohm’s Law to find the voltage across the \(6\,\Omega\) resistor:
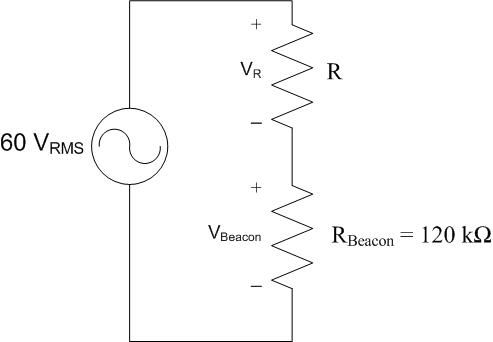
An AC-powered electric fan, modeled as a 150 \(\Omega\) resistor, is plugged into a \(120\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) outlet. The fan requires \(90\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) to operate, so a resistor is added to form a voltage divider.
Given:
\(V_{S} = 120\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\)
\(R_{fan} = 150\ \Omega\)
Find the resistor value \(R\) to provide the fan with \(90\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\).
Solution:
The resistor \(R_{\text{adapter}}\) will drop some of the voltage, but we first need to determine its value. We can find this using the voltage divider equation.
In this case, we know
We solve the voltage divider equation for \(R_{\text{adapter}}\):
Substituting values,
Therefore,
