Practice Problems#
Plot the following equations:
a)
\(v(t) = -2 + 2\cos(360^\circ \cdot 100\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\)
b)
\(v(t) = 2\cos(360^\circ \cdot 10\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\)
c)
\(v(t) = 4\cos(360^\circ \cdot 1\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\)
d)
What equation is associated with the graph?
e)
What equation is associated with the graph?
If
\(v_{S}(t) = 4 + 8\cos(360^\circ \cdot 10\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\),
graph \(i_{X}(t)\) for the signal below.
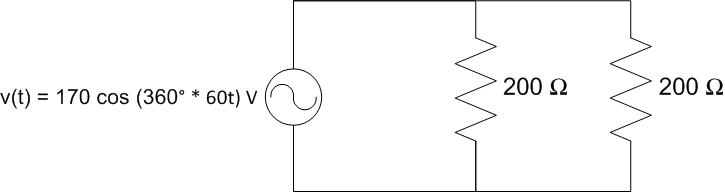
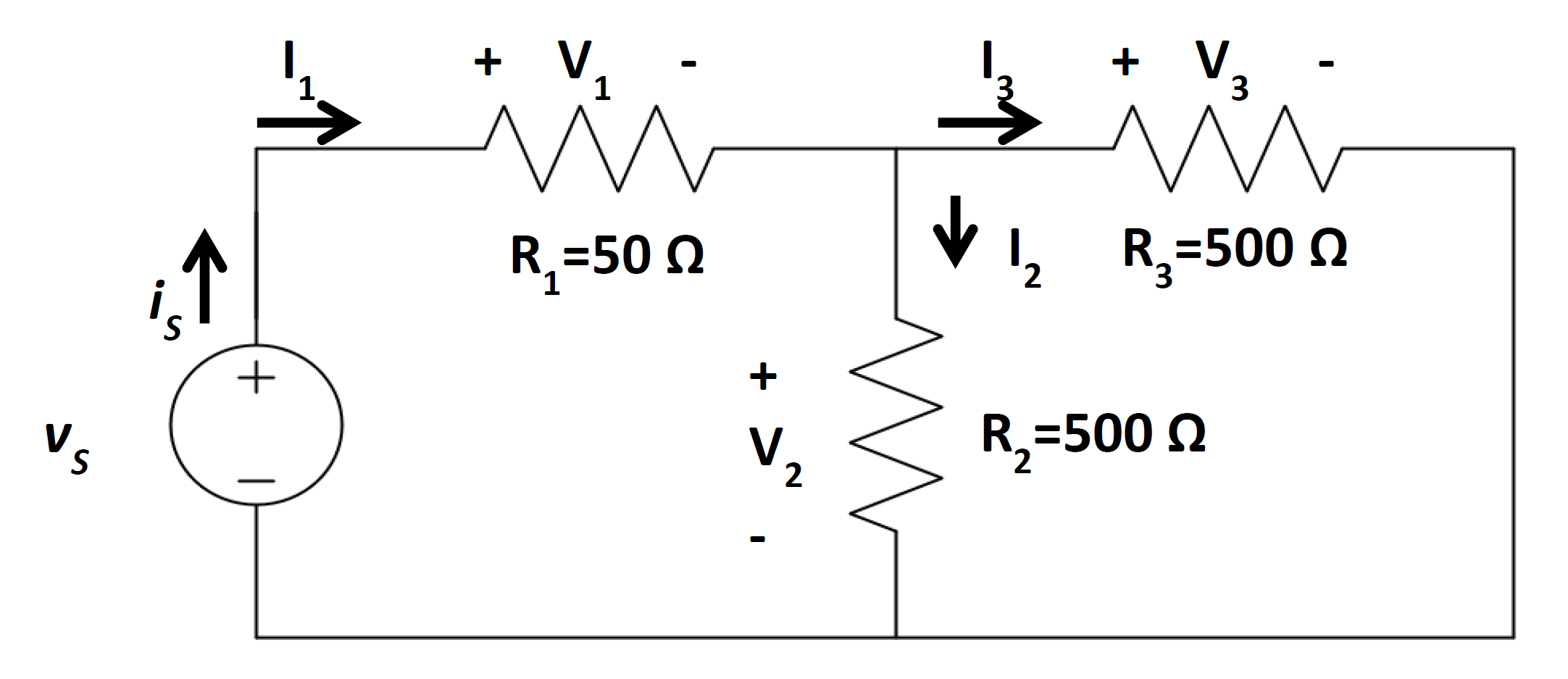
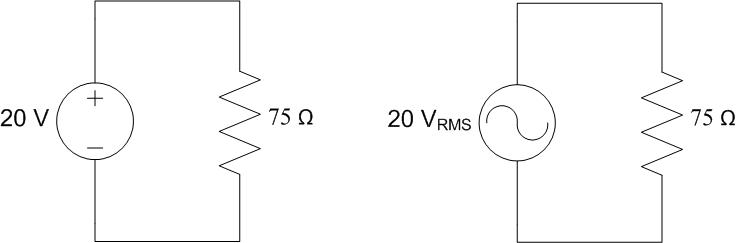
Find the power consumed by the circuit below given
\(V_{S} = 1.5\ \mathrm{V}\).
Find the average power consumed by the circuit below given:
\(v_{S}(t) = 2.12\cos(360^\circ \cdot 100\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\)
Compare the power consumed by the two circuits above. What can you say about the power consumed?
What is \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{Hz}}\) equivalent to?
a. s
b. 1/s
c. f
d. None of the above
A 9 V battery is connected to a resistor that consumes 7.22 mW of power. Which of the following AC sources would cause the same resistor to consume 7.22 mW of average power?
a. \(7.22\cos(360^\circ \cdot 2\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\)
b. \(9\cos(360^\circ \cdot 2\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\)
c. \(7.22\ \mathrm{mV}_{RMS}\)
d. \(9\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\)
A B-52 generator produces the signal
\(v(t) = 290\cos(360^\circ \cdot 400\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{V}\).
a. Graph this signal as a function of time.
b. What is the RMS voltage for the generator above?
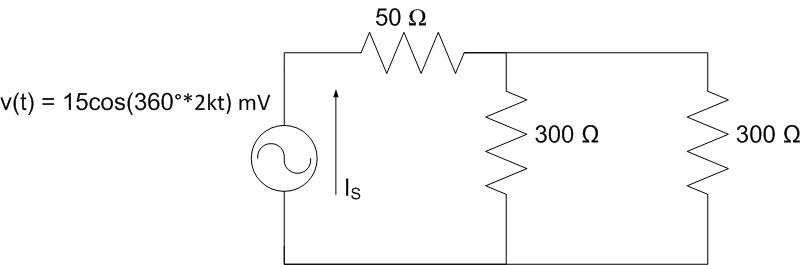
The fuse for a 2000-lb general-purpose bomb includes a spinner producing
\(v(t) = 15\cos(360^\circ \cdot 2\ \mathrm{kHz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{mV}\).
The arming circuit is modeled as three resistors, as shown below. Graph the current signal coming out of the spinner, \(I_{S}(t)\).
Which of the two sources below produces more average power?
The circuit below has a current source providing
\(i(t) = 11.75\cos(360^\circ \cdot 50\ \mathrm{Hz} \cdot t)\ \mathrm{A}\).
Find \(v_{1}(t)\).
An AC-powered electric fan, modeled as a 150 \(\Omega\) resistor, is plugged into a standard \(120\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) wall outlet. Since the fan requires \(90\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) to operate, a resistor is added to form a voltage divider.
Given:
\(V_{S} = 120\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\)
\(R_{fan} = 150\ \Omega\)
Find the resistor value \(R\) required to provide the fan with \(90\ \mathrm{V}_{RMS}\).
