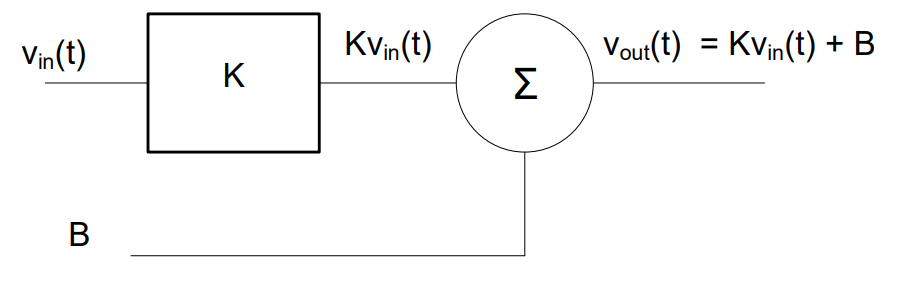
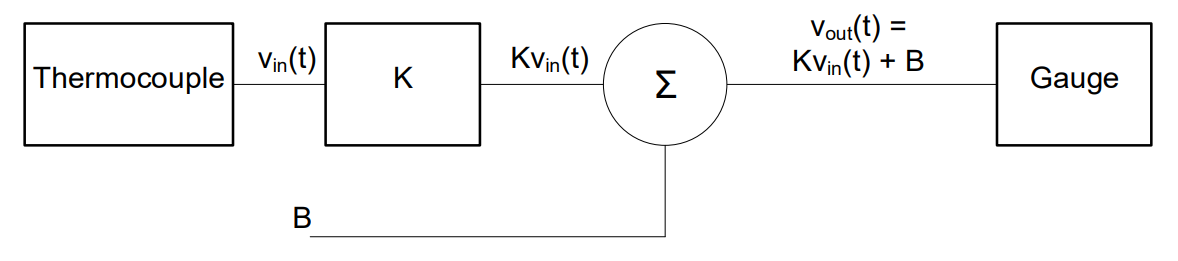
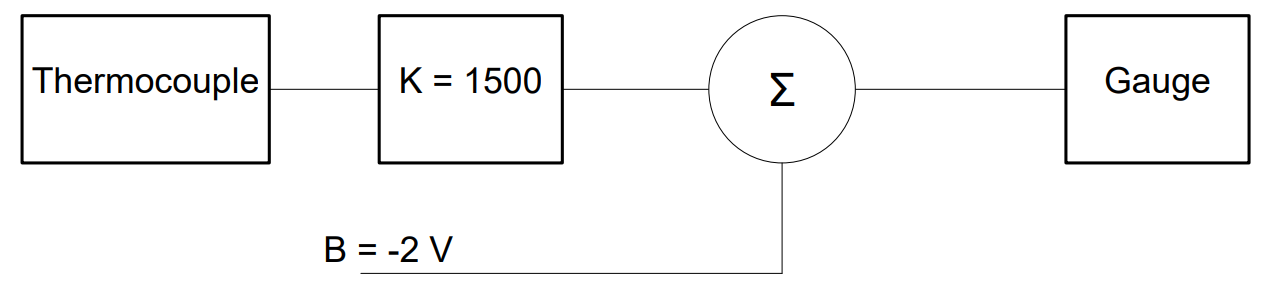
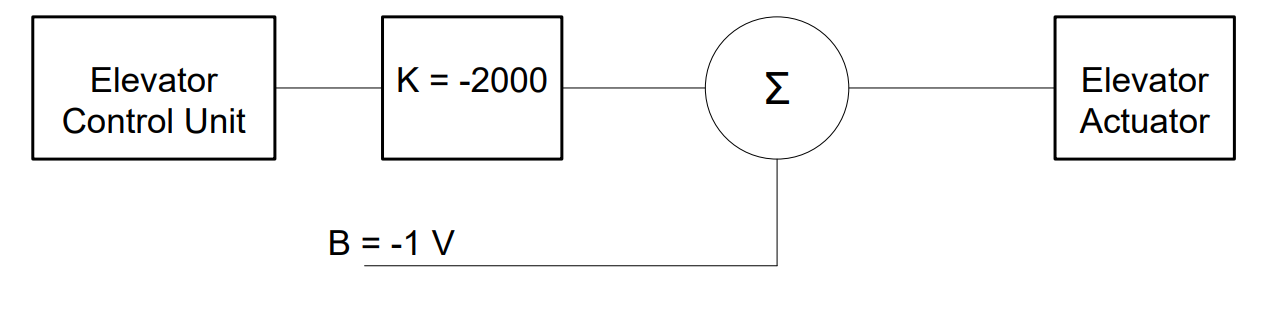
Practice Problems (KEY)#
Answer the following questions about the devices shown in the table below.
Device |
Current |
Voltage |
|---|---|---|
A |
3 \(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\) |
190 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) |
B |
8 \(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\) |
190 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) |
C |
3 \(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\) |
190 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) |
X |
10 \(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\) |
40 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) |
Y |
4 \(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\) |
40 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) |
Z |
5 \(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\) |
40 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) |
a. Draw the block diagram to represent this set of devices.
b. Label circuit breaker locations and values.
c. Calculate total power supplied.
Calculate the following for the power distribution system below:
a. Turns ratio of the transformer
b. Circuit breaker values for circuit breakers A, B, and C
c. Power the source produces
T/F Buses work by delivering power to devices connected in series.
T/F A circuit breaker works the same as a fuse in that it opens when current exceeds the breaker’s rating.
The electrical system for a small reconnaissance aircraft is shown below. The aircraft has two buses, one at 160 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) and one at 50 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\), powered by a 160 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) alternator.
a. What transformer turns ratio is required to drive the 50 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) bus?
b. Given the following table of required currents, what circuit breaker ratings would you choose for breakers A, B, C, and D?
Equipment |
Current (\(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\)) |
|---|---|
Flaps |
2.5 |
Avionics |
4 |
Navigation |
6 |
Comm |
3.5 |
Camera |
4.5 |
The electrical system for a fighter is shown below. The aircraft has two buses, one at 80 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) and one at 20 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\), powered by a 115 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) alternator.
a. What transformer turns ratios are required?
b. Given the following table, how much power must the alternator provide?
Equipment |
Current (\(\mathrm{A}_{RMS}\)) |
|---|---|
Flaps |
5 |
Landing Gear |
8 |
Radar |
4 |
Computer |
2 |
IRS |
5 |
Alternatively,
The electrical system for a fighter is shown below. The aircraft has two busses, one at 80 VRMS and one at 20 VRMS, powered by a 115-VRMS alternator.
a. What transformer turns ratios are required to drive the two buses?
b. Given the following table of required currents, how much power must the alternator provide?
Equipment |
Current (\(A_{\text{RMS}}\)) |
|---|---|
Flaps |
5 |
Landing Gear |
8 |
Radar |
4 |
Computer |
2 |
IRS |
5 |
An aircraft requires a 205 \(\mathrm{V}_{RMS}\) bus and a 32 V DC bus. Calculate the transformer turns ratio and breaker values for breakers A and B. The Comm draws 4 A and the Camera draws 5 A. The AC–DC converter efficiency is 80%.
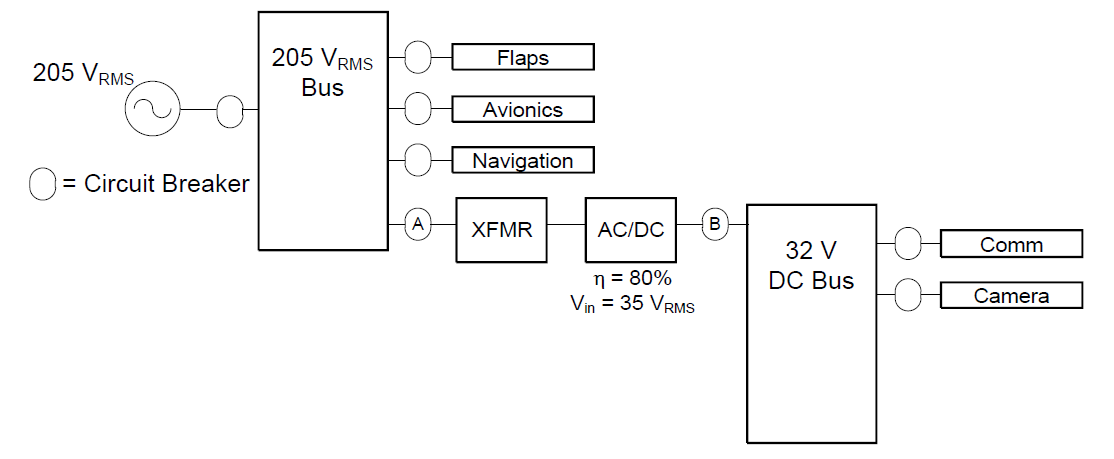
Solution#
1) Compute the transformer turns ratio#
The AC–DC converter input voltage is given in the diagram as an RMS value, so we can use RMS voltages directly:
\(a=\dfrac{V_1}{V_2}=\dfrac{205}{35}=5.86\)
2) Size the breaker at location B#
The comm and camera current draws are given:
\(I_{\text{Comm}} = 4~\text{A}\)
\(I_{\text{Camera}} = 5~\text{A}\)
So the breaker at B must be larger than:
\(I_B > 4+5 = 9~\text{A}\)
Choose the next standard value:
CB at B: 10 A
3) Compute DC load power on the 32 V bus#
\(P_{\text{Comm}} = (32~\text{V})(4~\text{A}) = 128~\text{W}\)
\(P_{\text{Camera}} = (32~\text{V})(5~\text{A}) = 160~\text{W}\)
Total DC power:
\(P_{\text{DC,total}} = 128 + 160 = 288~\text{W}\)
4) Account for AC–DC converter efficiency (80%)#
\(P_{\text{in,ACDC}} = \dfrac{288~\text{W}}{0.8} = 360~\text{W}\)
This is the power on the transformer secondary side feeding the AC–DC converter.
Assuming an ideal (lossless) transformer:
\(P_{\text{primary}} = P_{\text{secondary}} = 360~\text{W}\)
5) Compute transformer primary current#
Primary voltage is \(205~\text{V}_{\text{RMS}}\), so:
\(I_{\text{XFMR}} = \dfrac{360~\text{W}}{205~\text{V}_{\text{RMS}}} = 1.75~\text{A}\)
Apply a 10% margin:
\(I_{\text{CB}} = 1.75 \times 1.1 = 1.925~\text{A}\)
Choose a standard breaker value:
CB at I: \(\approx 2~\text{A}\)
Is the retrofit design below valid? Why or why not?
No, this is not a good design. The added transformer is connected to a DC bus, and transformers only operate with AC (they require a changing magnetic field). With DC input, the transformer will not transfer power, so there will be no usable voltage or current on the secondary side. As a result, the 5 V bus will not receive any power. econdary, and the 5 V bus will receive no power.
How many breakers should be added to the building security system below, and where?
Solution#
Because every component is critical to the system, you don’t want a single fault to take down an entire bus—or, worse, the whole system.
Per-load protection (required):
Install a dedicated breaker for each load connected to the 60 V and 25 V buses.Total: 8 breakers
Bus-level protection (recommended):
Add breakers upstream of each bus to protect against excessive combined bus current draw.Total: +2 breakers (now 10)
Additional isolation (optional, “belt and suspenders”):
Consider extra breakers:Between XFMR2 and the ADC
On either side of the transformers
This helps isolate internal shorts or failures within the ADC or transformers.Total: up to +3 breakers (up to 13)
Final count: plan for 10–13 breakers
10 = baseline configuration
13 = more robust / optimal configuration
