Concept Flashcards#
What is Vbias in an AC signal?
The DC component of the signal (Vbias is the average value of the waveform).What is Vm in an AC signal?
The amplitude of the AC signal – the peak deviation from its average (DC) level.What is f in an AC signal?
The frequency of the signal, defined as the number of cycles per second and measured in hertz (Hz).What is t in an AC signal?
Time, measured in seconds, and used as the independent variable.What is φ (phi) in an AC signal?
The phase shift of the signal – it indicates how much the waveform is shifted in time relative to 𝑡 = 0 (in degrees or radians).What is T in an AC signal?
The period – the time it takes to complete one full cycle. It is the reciprocal of frequency:T = 1 / f.What is τ (tau) in an AC signal?
he time delay of the waveform’s start – essentially the phase shift expressed in time. It’s the time from 𝑡 = 0 to the first positive peak, found by converting the phase angle into seconds.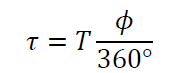
What are the key items that must be identified when graphing an AC signal?
- Vmax and Vmin (defined by Vm)
- The signal period (T)
- Any DC bias
- Any phase shift
Explain this AC signal chart to yourself.
Did you correctly identify Vm, T, Vbias, and any phase shift?
What is instantaneous power?
The power at a given moment in time is calculated by
\[
p(t) = v(t)\, i(t)
\]
where \(p(t)\) is the instantaneous power, \(v(t)\) is the instantaneous voltage, and \(i(t)\) is the instantaneous current at that moment.
What is Vrms?
The root-mean-square value of an AC signal – it is the equivalent DC value that would produce the same average power in a resistor. (In other words, the “effective” voltage or current of the AC.).How do you calculate average power in an AC circuit?
For a sinusoidal AC signal with voltage and current in phase (such as across a resistor),
\[
P_{\text{avg}} = V_{\text{rms}}\, I_{\text{rms}}
\]
